- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
CST2013: Discrete Face Port
 Simulation: Sources and Loads
Simulation: Sources and Loads  Discrete Port
Discrete Port
Beside waveguide ports or plane waves the discrete ports offer another possibility to feed the calculation domain with power. The discrete face port is one kind of discrete port. It is supported by the integral equation solver, the transient solver, as well as the frequency domain solver with tetrahedral mesh. The discrete face port is replaced by a Discrete Edge Port if any other solver is chosen. Two different types of discrete face ports are available, considering the excitation as a voltage or as an impedance element which also absorbs some power and enables S-parameter calculation.
Please refer to the Discrete Port Overview page to find some more detailed information especially regarding the construction procedure.
Properties frame
Port type: Select here the type of the discrete face port. Corresponding to this setting the input parameters in the properties frame will change. Please note, that the input signal for the port is normalized differently, depending on the chosen port type.
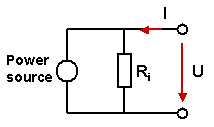
S-Parameter: This port type is modeled by a lumped element, consisting of a current source with an inner impedance, which excites and absorbs power. The current source will only be active, when the discrete element is the stimulation port in the analysis. This port realizes an input power of 1W and enables the calculation of correspondent S-parameter. In addition it is also possible to monitor the voltage across and the current through the discrete face port. Note that the orientation of the discrete face port is used to determine the phase of the S-parameters. An equivalent circuit diagram for a discrete face port of the S-parameter type is shown below.
Voltage: This port type realizes a voltage source, exciting with a constant voltage amplitude. In case that this port is not stimulated in the analysis the voltage along the wire is set to zero. The voltage excitation signal will be recorded during the solver run.
Current: This port type realizes a current source, exciting with a constant current amplitude. The current excitation signal will be recorded during the solver run.
Name: Select a valid name from the drop down list. This number will be displayed next to the discrete face port in structure plots and will be used for naming the S-parameter results. Please note that the port numbers are shared with the waveguide port definitions.
Label: Here, you may define a label for the port.
Impedance / Voltage / Current: Specify a numerical expression for the input parameter of the discrete face port. Insert either impedance, voltage amplitude or current amplitude due to the settings made in the port type frame. In case of the S-parameter selection the resulting S-parameters will be automatically normed to the specified impedance.
Monitor voltage and current: If this option is activated, the voltage across and the current through the discrete face port are monitored during the simulation. The resulting curves are placed in the navigation tree folder 1D Results  Discrete Ports
Discrete Ports  Voltages and 1D Results
Voltages and 1D Results  Discrete Ports
Discrete Ports  Currents, respectively.
Currents, respectively.
Please note that the spectral amplitude results represent peak values and are normalized to the spectrum of the defined reference signal. In case of the S-parameter discrete port type, all results refer to an input power of 1 W.
Location frame
If the discrete face port is replaced by a Discrete Port this start and end point are taken for the Discrete Port. An extra point can be picked which determines the position of the discrete edge port if the discrete face port is created by two closed edge chains.
Excitation at center edge: The excitation takes place at the center edge of the port by default or the user picked edges and edge chains respectively.
Invert Direction: Changes the direction of the discrete face port.
Use projection on edge: When this check box is activated then one edge is projected onto the other edge and the discrete face port is created in between the edge and its projection.
Reverse projection: Changes the edges used for the projection. That means if the check box is activated then the second picked edge is projected onto the first picked edge. This option is only available when Use projection on edge is active.
OK
Stores the current settings and leaves the dialog box.
Preview
Press this button to create a preview of the port. This option is very useful to check the settings before you actually create the port.
Cancel
Closes this dialog box without performing any further action.
Help
Shows this help text.
Discrete Port Overview, Discrete Port, Waveguide Port, Reference Value and Normalization,
CST微波工作室培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您快速学习掌握CST设计应用
上一篇:CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver Parameters - Resonant: Fast S-Parameter
下一篇:CST2013: Define Heat Source
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- CST2013: Mesh Problem Handling
- CST2013: Field Source Overview
- CST2013: Discrete Port Overview
- CST2013: Sources and Boundary C
- CST2013: Multipin Port Overview
- CST2013: Farfield Overview
- CST2013: Waveguide Port
- CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver
- CST2013: Import ODB++ Files
- CST2013: Settings for Floquet B
