- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
HFSS15: Assigning Lumped Ports for Modal Solutions
1. Select a surface to which you want to assign the port and click HFSS or HFSS-IE>Excitations>Assign>Lumped Port to bring up the Lumped Port dialog.
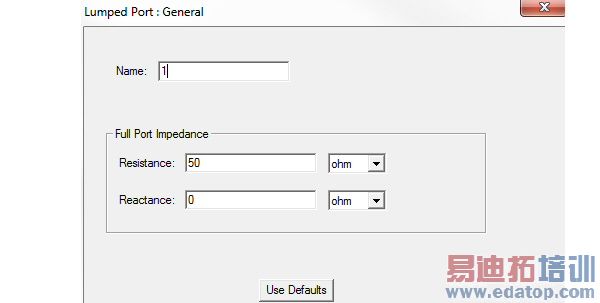
2. Define the complex Full Port Impedance in the Resistance and the Reactance text boxes.
You can assign a variable to these values. This variable can be dependent on the frequency, which allows use of a dataset for frequency dependent impedance.
3. Click Next to display the Lumped Port: Modes window. The number of Modes is not editable.
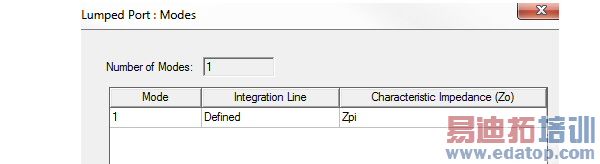
4. Follow the directions for defining an integration line.
The Characteristic Impedance (Zo) column shows the Zpi method usually used to calculate the characteristic impedance. However, if there are no conductors on the port and Zpi is near zero, HFSS uses Zpv.
For definitions of how HFSS defines these values, see Calculating the PI Impedance, and Calculating the PV Impedance.
5. Click Next or the Post Processing tab to display the Lumped Port: Post Processing window. Values here affect S-Parameters only. By default, lumped ports are renormalized to a 50 Ohm full port impedance. To specify a renormalization impedance, select Renormalize All Modes and type a value in the Full Port Impedance text box. Select the corresponding unit in the drop down menu.
If you want to enter a complex impedance, enter it in the following form:
<re> + <im>j
If you do not want to renormalize the port impedance, select Do Not Renormalize.
6. If imperfect ports are used (internal lumped port), HFSS needs some port calibration (deembedding). If lump ports are used, parasitic inductance of port geometry can be removed through calibration or de-embedding
For HFSS single frequency solves,adaptive pass solutions, interpolating sweeps, and fast sweeps, if a lumped port has a single rectangular face, you have the option to check Deembed. The setting is not offered in transient or transient network analysis designs.

Checking Deembed enables analytic frequency dependent formulas that calibrate lumped ports, which can be thought of as "deembedding" the lumped port structure. Lumped port calibration is a post processing step, using port geometric parameters that are extracted and saved when solving. The calibration is also available for solution results produced prior to HFSS version 14, in which case the port geometric parameters are extracted and saved once per design variation at the time of the first matrix data load for it.
After possible interpolation, renormalization, and deembedding applied to the matrix data for each frequency, the calibration formulas modify the Z matrix and then compute a replacement for the post processed S and Y matrices. The same calibration applies when calculating adaptive convergence, since adaptive convergence is based on fully post processed matrices. The frequency dependent formulas are encapsulated within the loaded solution and used when it supplies frequency data. Solutions sent over to Designer via the dynamic link have the same support, based on exactly those lumped ports which were selected for this option.
The Deembed option can be turned on or off as a post processing operation without invalidating solutions. If multiple lumped ports are selected in the Excitations List panel, changes to the common Deembed property change the setting for all lumped ports at once, but only for those that support calibration.
If a port is selected for calibration but the validation checks fail for some variation (which could happen with a parametric solve), then the matrix data will not load for that variation. Also, if the fields are to include port post processing effects, then the fields do not load.
HFSS 学习培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您全面系统地学习掌握HFSS
上一篇:Assigning Excitations in HFSS-IE
下一篇:Assigning IE Regions


